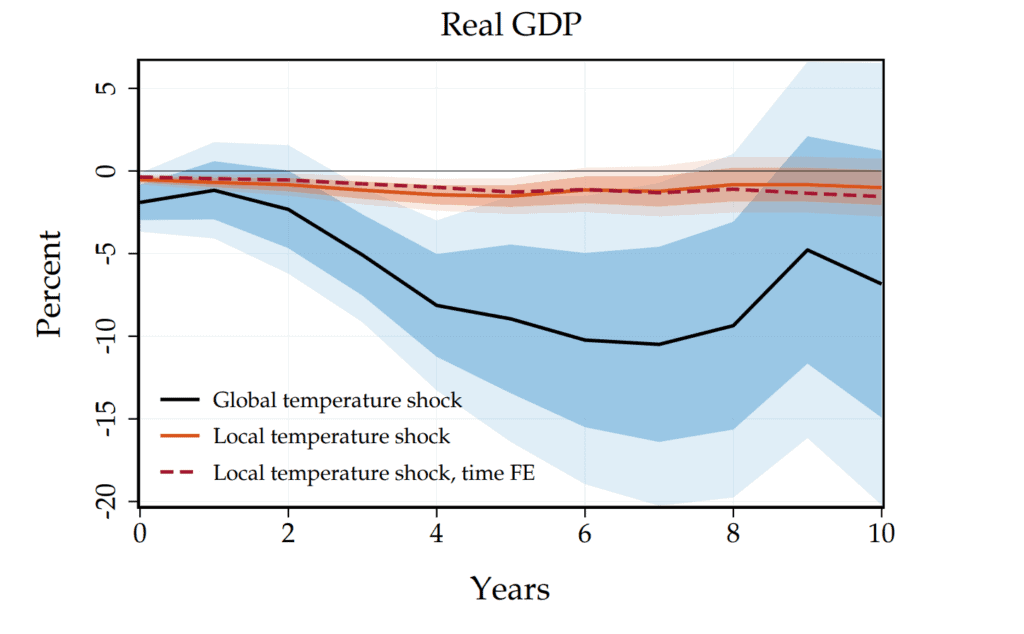
Recent publications show a 3°C climate change costs 36% of GDP or $56 trillion. That is like the depression of 1929, but forever. The article outlines a three-pronged approach of Mitigation Resilience and Renewal for Climate Change. There are scary changes underway that have a potential to decrease global GDP by 12% for every degree of global warming Previously it was thought 1° rise would reduce GDP by 2 trillion. New data shows that to be six times that.
Global GDP is about $100 trillion. So this means a $36 trillion decrease.
There will still be some economic growth happening but by the end of the century people may well be 50% poorer than they would’ve been if it wasn’t for climate change. Adrien Bilal Harvard
1. Immediate Mitigation and Adaptation
- Emission Reduction: This involves rapidly reducing greenhouse gas emissions from various sectors, including transportation, energy production, and industrial activities. Strategies such as transitioning to renewable energy sources, improving energy efficiency, and adopting sustainable practices are crucial.
- Ecological Restoration: Restoring degraded ecosystems like forests and wetlands can help absorb carbon dioxide and enhance biodiversity.
- Climate Adaptation: Preparing for the unavoidable impacts of climate change, such as rising sea levels, extreme weather events, and changes in agricultural patterns. This includes building resilient infrastructure, developing early warning systems, and promoting sustainable land use practices.

2. Resilience to Future Shocks
- Systemic Preparedness: Ensuring that critical infrastructure, such as power grids, transportation networks, and healthcare systems, are resilient to disruptions caused by climate change. This involves investing in robust designs, redundancy, and emergency response plans.
- Community Resilience: Building strong and supportive communities that can withstand and recover from climate-related disasters. This includes fostering social cohesion, promoting local food production, and developing community-based emergency response plans.
- Economic Diversification: Reducing dependence on industries vulnerable to climate change and promoting economic activities that are more resilient to climate impacts.
3. Foundations for Future Renewal
- Mindset Shifts: Fostering a collective shift in mindset towards interconnectedness, ecological stewardship, and long-term thinking. This involves promoting education, awareness campaigns, and cultural change.
- Regenerative Practices: Adopting practices that restore and enhance ecosystems, such as regenerative agriculture, permaculture, and ecological restoration.
- Ethical Consumption: Encouraging sustainable consumption patterns and supporting businesses that prioritize environmental and social responsibility.
- Governance and Policy: Developing effective governance structures and policies that promote sustainable development and address climate change challenges.
Interconnections and Synergies:
These three fields are interconnected and mutually reinforcing. For example, investing in renewable energy (mitigation) can create jobs and strengthen local economies (resilience), while promoting regenerative practices (foundation) can help reduce emissions and improve ecosystem health (mitigation).
A Holistic Approach:
Addressing the climate crisis requires a holistic approach that combines immediate actions to mitigate and adapt to climate change with long-term efforts to build resilience and create a sustainable future. By focusing on these three fields, we can work towards a more just, equitable, and sustainable world for generations to come.
Mitigation Resilience and Renewal for Climate Change
We need to accelerate the rate of change from fossil fuel to electricity, from molecular electricity to electron Climate crisis costs the world 12% in GDP for every 1°C temperature rise. In a paper [4] the macroeconomic impacts of climate change are six times larger than previously documented. The report authors relie on a time-series local projection approach to estimate the impact of global temperature shocks on Gross Domestic Product (GDP). This approach exploits natural variability in global mean temperature—the source of variation closest to climate change—which we show to predict damaging extreme climatic events much more strongly than country-level temperature. We find that a 1°C rise in global temperature lowers world GDP by 12% at peak.
References
- Between Optimism and Despair: The Messy Middle Paths Through Climate Breakdown Jamie Bristow. 2024 https://countercurrents.org/2024/08/between-optimism-and-despair-the-messy-middle-paths-through-climate-breakdown/
- Economic damage from climate change six times worse than thought – report The Guardian Aug 2024 https://www.theguardian.com/environment/article/2024/may/17/economic-damage-climate-change-report
- Ted Talk The tipping points of climate change — and where we stand https://www.stockholmresilience.org/research/research-videos/2024-08-19-the-tipping-points-of-climate-change—and-where-we-stand.html
- Climate crisis costs the world 12% in GDP for every 1°C temperature rise WEF https://www.weforum.org/agenda/2024/06/nature-climate-news-global-warming-hurricanes
- The Macroeconomic Impact of Climate Change: global vs local temperature Aug 2024 Adrien Bilal Diego R. Känzig https://www.nber.org/system/files/working_papers/w32450/w32450.pdf
- Arctic Sea Ice minimum 2024. Three degrees Celsius warming now baked in! Just have a think. https://youtu.be/tO_ZHg5OCAg?si=J49E_hZCNFNzIfj7
- The Tipping Points of Climate Change — and Where We Stand | Johan Rockström | TED https://youtu.be/Vl6VhCAeEfQ?si=a4Fc41191XXfs3uc